Gull Control
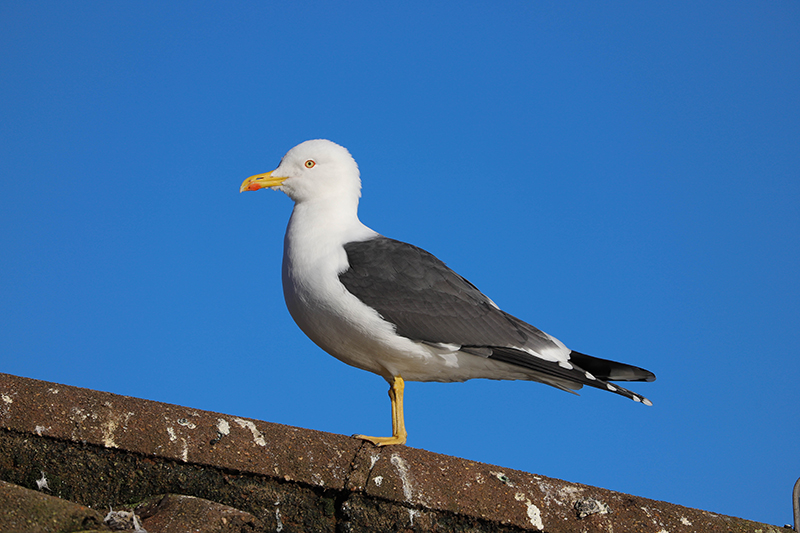

Gulls (Laridae) is the generic name that covers a few species but the usual ones causing problems are Herring gull (Larus argentatus) and Lesser black-backed gull (Larus fuscus). Commonly refered to as seagulls, these coastal birds are increasingly found in towns and cities, or anywhere that has available food. Effective gull control requires an integrated approach and, as specialists in gull control, we can recommend and implement the most effective methods available for the control and management of gulls. All our gull control is carried out under license.
Gulls tend to nest on either flat / shallow pitch roofs or where there is an anchor point on the roof, such as behind a chimney.
Gull Biology and Behaviour
- Commonly refered to as seagulls, gulls are actually coastal birds
- Gulls have a life-span of thirty years+
- They like to build their nests on roofs
- Gulls usually lay two to three eggs in April and May, which take approximately 30 days to hatch and then can fly after about 10 days
- Gulls sometimes will ‘double-clutch’ which means they will lay a second time in July and August
Free Survey
We will survey your site free of charge, and talk to the people involved to ensure that we understand your bird problem. We then complete a comprehensive report that outlines the options available to you, and specifies our recommended solution as well as detailing all the costs involved.
Management and Control of Gulls
Gulls will be on your site for nesting predominantly. When nesting they can become very aggressive leading to some no-go areas on your roof or even parts of your site.
Hawk Flying
Hawk flying for gull control is a non-lethal deterrent programme, a natural and effective measure, where the aim is not to kill the gulls but to deter them from the area. The public is supportive of hawk flying for gull control, and our clients benefit from positive public relations by dealing with the problems caused by nuisance gulls in a humane and responsible way.
Unlike other bird scaring devices, gulls never become habituated to the presence of a live bird of prey.
Gull Proofing a Building or Area
The most effective way to prevent the problems being caused by nuisance gulls is to install a proofing solution. Installing anti-gull nets, or anti-gull spikes will prevent gulls being able to nest, perch or roost on the structure.
The proofing solution installed may be complex and require several systems to achieve the best possible overall effect. Acting as your trusted partner, our surveyors are free to select any products or systems on the market, from any manufacturer, to achieve the desired effect as well as commissioning bespoke manufactured systems. We select the most suitable systems from the entire range available. All installations are completed by our own fully trained staff utilising the services of specialists where required.
Gull Scaring Systems
Scaring systems, whether that is an audio or visual gull scaring system do not work very well for very long. Gulls adapt very quickly to new things, so scaring systems will have very little long-term effect on a gull population.
Self Help Measures
The most important thing you can do to discourage gulls is to remove access to food. Ensure that all bins are adequately covered and clean up any food spillages. Do not feed the gulls, and ask everyone using your premises to refrain from feeding the gulls.
Gulls, by their nature, will spend much of their time at height, on the top of the building. They come down to ground level mainly to feed, and gulls can be seen feeding in large flocks where food is available.
Signs that you may have a gull problem include
- Seeing lots of gulls (seagulls) on the roof
- Hearing gulls from inside your property, especially hearing the cries of young gulls wanting their parents to feed them
- Finding nesting materials around
- Damage to property or stock
- Blocked drains or gutters, especially if there are gull feathers and nesting materials
- Gull fouling / droppings at ground level
- Discarded food, including take-away food such as chicken bones generally around the area